
Paul Gauguin Giclée Fine Art Prints 3 of 8
1848-1903
French Post-Impressionist Painter
Paul Gauguin was a French Post-Impressionist Painter (Paris 1848-Atuona Marquesas Islands 1903).
Paul Gauguin was a traveller by nature. His artistic career marked a transition from Impressionism to Symbolism. He had a major influence on Fauvists and Expressionists through his colors and forms.
Paul Gauguin's taste for the unknown was evident from his childhood in Peru. After joining the navy in 1865, he was advised by his tutor Gustave Aroa (a painter) to leave the navy and work as a securities broker in Paris.
He attended the Filippo Colarossi academy and painted on Sundays. In 1873, he married the Danish Mette Sophie Gadd. They had five children. Camille Pizarro was a friend of Arosa and encouraged Gauguin, who had been exhibiting Impressionist paintings since 1879, to continue. He invited Gauguin to work with Jean-Baptiste Armand Guillaumin, and Paul Cezanne in Pontoise, where Gauguin's example inspired him to leave Impressionism.
Gauguin, who was forced to leave the bourse in 1883 by an economic crisis, first painted in Rouen where Pissarro, Claude Monet, and other wealthy art collectors kept in touch, before deciding on a business venture in Denmark. In 1885, he returned to Paris without his wife or children. He was destined to fail: he dreamed of business for many years, but his passion became painting.
Gauguin's first visit to Pont-Aven, in 1886, was marked by the exhibition of his paintings, including those he brought back from Rouen and Denmark, which were characterized by their muted, rich tones.
In the year following, while in Martinique, he planted some plants and painted pointillist paintings in which he revealed the exoticism of colour and the exoticism that his memories from Peru and his sea journeys had imprinted in his memory.
Gauguin made his second visit to Pont-Aven in 1888. Long discussions with the young Emile Bernard led to the development of a new aesthetic which contrasted neo impressionism and synthetism. (Pure colours laid flat with dark rings). Vision after the Sermon 1888 - or Jacob’s Struggle With the Angel is the most evident work.
During this time, Gauguin was a leading figure in the Symbolist movement. From November to December of 1888, he took a holiday with Vincent Van Gogh in Arles and created a series brilliant canvases ("Aliscamps"). Gauguin split from Van Gogh when the latter had a serious attack of mental illness. La Belle Angele and Le Christ vert reflect the moral and plastic problems of that period. His first trip to Tahiti, 1891-1893, followed.
Paul Gauguin lived in Europe and the Tropics. Polynesia gave him new creative energy, and he became the first great artist who studied and appreciated the arts that we now call primitive and handed them over to the West.
Gauguin said, "I'm going away to calm down and to be free of the influences of civilization," before sailing to Tahiti during the spring of 1891. "I must, for this purpose, immerse myself into the virgin nature [...], without any other concern than to transmit like a young child the conceptions in my mind by using the primitive art, which is the only good and the only true."
Gauguin found in Tahiti the world of his dreams, which was relatively unspoiled (Femmes de Tahiti 1891). Fearing intrigue as well as oblivion he returned to Paris once he had enough paintings to take part in an exhibition at Durand-Ruel.
Stéphane Malarmé was amazed to discover "so much brilliance in so many mysteries." He was visited by musicians as well as writers such August Strindberg and Charles Morris with whom he co-wrote his autobiography Noa Noa (1897).
Financial success, however, came slowly. Gauguin lost a case, sailors taunted Ana la Javan in Concarneau, and he left Europe in 1895, after a brawl.
Polynesia is where the confusion of Breton religious works gives way to massive forms and saturated colours in large, colourful forms. In 1896, the joy of returning home is reflected in the painting "Jours delicieux", and then grief takes over (Nevermore).
Gauguin is depressed and contemplates suicide after hearing of the death of his daughter Aline. Where are we from? What are we? His testament, Where Are we going (1897), became his book.
His renewed enthusiasm after moving to Atuona, on the island Hiva-Oa, in the Marquesas (in 1901) led him to produce masterpieces that express his vision of a paradisiacal world (Contes barbares, 1902). Gauguin created sculptures. Gauguin died at the age of just 55, exhausted by alcohol, illness and disputes with local authorities.
Paul Gauguin was a traveller by nature. His artistic career marked a transition from Impressionism to Symbolism. He had a major influence on Fauvists and Expressionists through his colors and forms.
Paul Gauguin's taste for the unknown was evident from his childhood in Peru. After joining the navy in 1865, he was advised by his tutor Gustave Aroa (a painter) to leave the navy and work as a securities broker in Paris.
He attended the Filippo Colarossi academy and painted on Sundays. In 1873, he married the Danish Mette Sophie Gadd. They had five children. Camille Pizarro was a friend of Arosa and encouraged Gauguin, who had been exhibiting Impressionist paintings since 1879, to continue. He invited Gauguin to work with Jean-Baptiste Armand Guillaumin, and Paul Cezanne in Pontoise, where Gauguin's example inspired him to leave Impressionism.
Gauguin, who was forced to leave the bourse in 1883 by an economic crisis, first painted in Rouen where Pissarro, Claude Monet, and other wealthy art collectors kept in touch, before deciding on a business venture in Denmark. In 1885, he returned to Paris without his wife or children. He was destined to fail: he dreamed of business for many years, but his passion became painting.
Gauguin's first visit to Pont-Aven, in 1886, was marked by the exhibition of his paintings, including those he brought back from Rouen and Denmark, which were characterized by their muted, rich tones.
In the year following, while in Martinique, he planted some plants and painted pointillist paintings in which he revealed the exoticism of colour and the exoticism that his memories from Peru and his sea journeys had imprinted in his memory.
Gauguin made his second visit to Pont-Aven in 1888. Long discussions with the young Emile Bernard led to the development of a new aesthetic which contrasted neo impressionism and synthetism. (Pure colours laid flat with dark rings). Vision after the Sermon 1888 - or Jacob’s Struggle With the Angel is the most evident work.
During this time, Gauguin was a leading figure in the Symbolist movement. From November to December of 1888, he took a holiday with Vincent Van Gogh in Arles and created a series brilliant canvases ("Aliscamps"). Gauguin split from Van Gogh when the latter had a serious attack of mental illness. La Belle Angele and Le Christ vert reflect the moral and plastic problems of that period. His first trip to Tahiti, 1891-1893, followed.
Paul Gauguin lived in Europe and the Tropics. Polynesia gave him new creative energy, and he became the first great artist who studied and appreciated the arts that we now call primitive and handed them over to the West.
Gauguin said, "I'm going away to calm down and to be free of the influences of civilization," before sailing to Tahiti during the spring of 1891. "I must, for this purpose, immerse myself into the virgin nature [...], without any other concern than to transmit like a young child the conceptions in my mind by using the primitive art, which is the only good and the only true."
Gauguin found in Tahiti the world of his dreams, which was relatively unspoiled (Femmes de Tahiti 1891). Fearing intrigue as well as oblivion he returned to Paris once he had enough paintings to take part in an exhibition at Durand-Ruel.
Stéphane Malarmé was amazed to discover "so much brilliance in so many mysteries." He was visited by musicians as well as writers such August Strindberg and Charles Morris with whom he co-wrote his autobiography Noa Noa (1897).
Financial success, however, came slowly. Gauguin lost a case, sailors taunted Ana la Javan in Concarneau, and he left Europe in 1895, after a brawl.
Polynesia is where the confusion of Breton religious works gives way to massive forms and saturated colours in large, colourful forms. In 1896, the joy of returning home is reflected in the painting "Jours delicieux", and then grief takes over (Nevermore).
Gauguin is depressed and contemplates suicide after hearing of the death of his daughter Aline. Where are we from? What are we? His testament, Where Are we going (1897), became his book.
His renewed enthusiasm after moving to Atuona, on the island Hiva-Oa, in the Marquesas (in 1901) led him to produce masterpieces that express his vision of a paradisiacal world (Contes barbares, 1902). Gauguin created sculptures. Gauguin died at the age of just 55, exhausted by alcohol, illness and disputes with local authorities.
179 Gauguin Artworks
Page 3 of 8

Giclée Canvas Print
$60.52
$60.52
SKU: 13115-GAP
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:66 x 88.9 cm
Philadelphia Museum of Art, Pennsylvania, USA
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:66 x 88.9 cm
Philadelphia Museum of Art, Pennsylvania, USA

Giclée Canvas Print
$71.05
$71.05
SKU: 13009-GAP
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:67 x 76 cm
Musee d'Orsay, Paris, France
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:67 x 76 cm
Musee d'Orsay, Paris, France

Giclée Canvas Print
$59.47
$59.47
SKU: 13129-GAP
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:89 x 124 cm
The State Hermitage Museum, St. Petersburg, Russia
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:89 x 124 cm
The State Hermitage Museum, St. Petersburg, Russia

Giclée Canvas Print
$66.98
$66.98
SKU: 13136-GAP
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:72.5 x 92 cm
Thyssen-Bornemisza Museum, Madrid, Spain
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:72.5 x 92 cm
Thyssen-Bornemisza Museum, Madrid, Spain

Giclée Canvas Print
$54.63
$54.63
SKU: 17774-GAP
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:79.2 x 51.3 cm
National Gallery of Art, Washington, USA
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:79.2 x 51.3 cm
National Gallery of Art, Washington, USA

Giclée Canvas Print
$68.35
$68.35
SKU: 19755-GAP
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:50 x 60 cm
Museum Langmatt, Baden, Switzerland
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:50 x 60 cm
Museum Langmatt, Baden, Switzerland

Giclée Canvas Print
$67.14
$67.14
SKU: 13157-GAP
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:75 x 65 cm
Finnish National Gallery, Helsinki, Finland
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:75 x 65 cm
Finnish National Gallery, Helsinki, Finland

Giclée Canvas Print
$54.63
$54.63
SKU: 13096-GAP
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:46 x 38 cm
Musee d'Orsay, Paris, France
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:46 x 38 cm
Musee d'Orsay, Paris, France

Giclée Canvas Print
$65.18
$65.18
SKU: 12989-GAP
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:92 x 73 cm
Albright-Knox Art Gallery, Buffalo, USA
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:92 x 73 cm
Albright-Knox Art Gallery, Buffalo, USA

Giclée Canvas Print
$63.22
$63.22
SKU: 12992-GAP
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:87 x 114 cm
New Carlsberg Glyptotek, Copenhagen, Denmark
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:87 x 114 cm
New Carlsberg Glyptotek, Copenhagen, Denmark

Giclée Canvas Print
$72.11
$72.11
SKU: 3010-GAP
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:67 x 76.5 cm
The State Hermitage Museum, St. Petersburg, Russia
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:67 x 76.5 cm
The State Hermitage Museum, St. Petersburg, Russia

Giclée Canvas Print
$60.67
$60.67
SKU: 13164-GAP
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:68 x 92 cm
The State Hermitage Museum, St. Petersburg, Russia
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:68 x 92 cm
The State Hermitage Museum, St. Petersburg, Russia

Giclée Canvas Print
$63.22
$63.22
SKU: 2990-GAP
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:74.5 x 94.5 cm
E.G. Buhrle Foundation Collection, Zurich, Switzerland
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:74.5 x 94.5 cm
E.G. Buhrle Foundation Collection, Zurich, Switzerland

Giclée Canvas Print
$55.85
$55.85
SKU: 2997-GAP
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:130 x 91.5 cm
Museum Folkwang, Essen, Germany
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:130 x 91.5 cm
Museum Folkwang, Essen, Germany

Giclée Canvas Print
$64.73
$64.73
SKU: 3043-GAP
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:72 x 92 cm
Pushkin Museum of Fine Arts, Moscow, Russia
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:72 x 92 cm
Pushkin Museum of Fine Arts, Moscow, Russia

Giclée Canvas Print
$57.66
$57.66
SKU: 3006-GAP
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:134 x 95 cm
Pushkin Museum of Fine Arts, Moscow, Russia
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:134 x 95 cm
Pushkin Museum of Fine Arts, Moscow, Russia

Giclée Canvas Print
$54.63
$54.63
SKU: 13011-GAP
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:49 x 38.5 cm
Bridgestone Museum of Art, Tokyo, Japan
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:49 x 38.5 cm
Bridgestone Museum of Art, Tokyo, Japan

Giclée Canvas Print
$63.22
$63.22
SKU: 3000-GAP
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:92 x 73 cm
Musée des beaux-arts, Liege, Belgium
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:92 x 73 cm
Musée des beaux-arts, Liege, Belgium

Giclée Canvas Print
$54.63
$54.63
SKU: 13102-GAP
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:38.4 x 46.4 cm
Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York, USA
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:38.4 x 46.4 cm
Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York, USA

Giclée Canvas Print
$64.88
$64.88
SKU: 13135-GAP
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:92 x 72.5 cm
Thyssen-Bornemisza Museum, Madrid, Spain
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:92 x 72.5 cm
Thyssen-Bornemisza Museum, Madrid, Spain

Giclée Canvas Print
$68.20
$68.20
SKU: 13093-GAP
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:72 x 58 cm
Musee des Beaux Arts, Grenoble, France
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:72 x 58 cm
Musee des Beaux Arts, Grenoble, France

Giclée Canvas Print
$54.63
$54.63
SKU: 3001-GAP
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:73 x 94 cm
Musee d'Orsay, Paris, France
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:73 x 94 cm
Musee d'Orsay, Paris, France
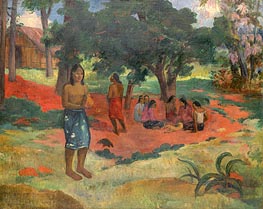
Giclée Canvas Print
$65.63
$65.63
SKU: 13125-GAP
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:77.2 x 96.5 cm
Yale University Art Gallery, Connecticut, USA
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:77.2 x 96.5 cm
Yale University Art Gallery, Connecticut, USA

Giclée Canvas Print
$64.28
$64.28
SKU: 17777-GAP
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:74 x 95.3 cm
National Gallery of Art, Washington, USA
Paul Gauguin
Original Size:74 x 95.3 cm
National Gallery of Art, Washington, USA